Does Medicare cover ablation for AFib? This exploration delves into the intricacies of Medicare coverage for atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation procedures, providing a thorough understanding of the process and potential outcomes. This detailed account will illuminate the criteria Medicare uses to determine coverage decisions, examining the factors influencing those decisions and exploring the support available to patients navigating this complex landscape.
This discussion will be a guide for patients seeking answers about the procedure and its potential financial implications under Medicare. It will encompass detailed explanations of the AFib ablation process, its risks, and the different types of procedures. Furthermore, it will analyze the specific conditions under which Medicare may cover these procedures, examining the role of physician documentation and pre-authorization requirements.
Real-life examples will illustrate both successful and unsuccessful claims. Finally, the guide will provide valuable resources and support for patients navigating the Medicare coverage process.
Introduction to Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Does Medicare Cover Ablation For Afib
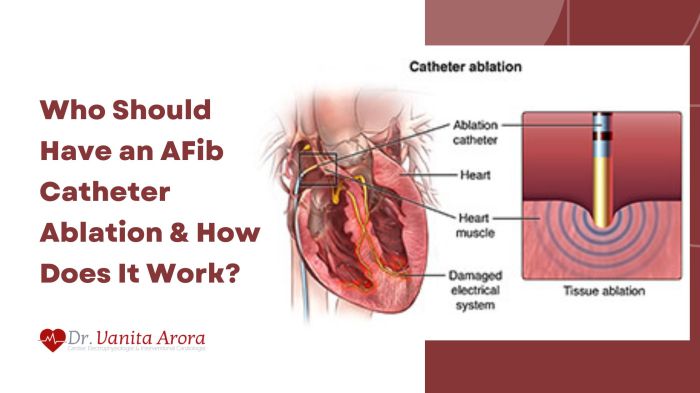
AFib, or atrial fibrillation, is a super common heart condition where the heart’s upper chambers quiver instead of beating smoothly. Think of it like a chaotic dance party in your heart – it’s not good for blood flow and can lead to serious issues. This irregular heartbeat affects millions worldwide, causing everything from fatigue to stroke risk. Getting a handle on AFib is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart.Catheter ablation is a procedure where doctors use tiny, flexible tubes (catheters) guided through blood vessels to reach the heart.
These catheters have special tools to zap problem areas in the heart that are causing the erratic electrical signals responsible for AFib. It’s like fixing a faulty circuit in your heart’s electrical system. The goal is to restore a normal heartbeat. While it’s a pretty advanced procedure, it’s a common treatment option for many AFib patients.
Catheter Ablation Procedure Details
The procedure typically involves inserting catheters into a vein in the groin or arm, guiding them to the heart. Specialized mapping tools pinpoint the specific areas causing the AFib. Then, radiofrequency energy or cryoablation is used to destroy these problem areas. The exact method used depends on the specific type of AFib and the doctor’s judgment. Recovery time varies, but many patients can return to their normal activities within a few weeks.
Different Types of AFib Ablation Procedures
Different ablation techniques target different parts of the heart. The choice of method depends on factors like the type and location of the AFib.
| Procedure Type | Description | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Radiofrequency Ablation | Uses heat to destroy the abnormal heart tissue. | Bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding healthy tissue, and temporary heart block. |
| Cryoablation | Uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy the abnormal heart tissue. | Bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding healthy tissue, and temporary heart block. |
| Pulmonary Vein Ablation | Targets the pulmonary veins, which are crucial for blood flow to the lungs. | Bleeding, pulmonary vein stenosis (narrowing), and possible need for additional procedures. |
This table provides a general overview. Specific complications and their likelihood can vary based on individual factors and the complexity of the case. Each procedure has unique advantages and potential side effects, which should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Medicare Coverage for Medical Procedures
Medicare, the healthcare program for seniors and some disabled folks, has specific rules for covering medical procedures. It’s not a simple yes or no; there’s a whole process behind deciding what gets covered. Knowing the rules can save you a ton of headaches when dealing with medical bills.
General Principles of Medicare Coverage
Medicare’s coverage isn’t universal; it’s a system of eligibility and requirements. Essentially, it covers a significant portion of medically necessary procedures but has limitations. Medicare has different parts (A, B, C, and D) each with its own rules and costs. Part A covers inpatient care, Part B covers doctor visits and outpatient services, and Part C (Medicare Advantage) combines Parts A and B, often with extra benefits.
Part D covers prescription drugs. It’s crucial to understand which part applies to a specific procedure.
Criteria for Coverage Decisions
Medicare uses a set of criteria to determine whether a procedure is covered. These factors are often intertwined, and a procedure might need to meet multiple criteria. The most important factors include:
- Medical Necessity: The procedure must be deemed medically necessary by Medicare’s guidelines. This means it’s the appropriate and most effective treatment for a specific condition. A simple example: If a less invasive treatment exists, Medicare might not cover a more extensive procedure.
- Approved Medical Guidelines: The procedure should align with recognized medical guidelines and best practices established by professional organizations. For example, if a new treatment method lacks sufficient evidence to support its widespread use, Medicare may be hesitant to cover it.
- Established Treatment: The procedure must be a recognized and established treatment for the specific condition. Novel, experimental, or unproven methods might not be covered.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Medicare considers the cost of the procedure in relation to its potential benefits. A procedure with a high cost and minimal benefit might not be covered.
Factors Influencing Coverage Decisions
Numerous factors influence Medicare’s coverage decisions for specific procedures. These factors can vary significantly, and each case is reviewed individually.
- Type of Procedure: Some procedures, like routine checkups, are routinely covered, while others, like experimental therapies, are not. A simple example: a routine colonoscopy is often covered, while a specific experimental gene therapy might not be.
- Patient’s Condition: Medicare’s coverage depends heavily on the severity and specifics of the patient’s condition. A simple infection is covered differently from a complex heart condition.
- Provider’s Qualifications: The qualifications and experience of the medical professional performing the procedure are also considered. A specialist in a particular area might have a greater chance of having a procedure covered than a general practitioner.
- Geographic Location: Accessibility to similar procedures and the prevalence of specific conditions in a region can also influence coverage decisions. For instance, a procedure commonly performed in an urban area might be covered more readily than one in a rural setting with limited resources.
Example Table: Common Procedures and Medicare Coverage
This table is a simplified overview; it’s crucial to consult with Medicare or a qualified professional for specific procedures.
| Procedure | Typical Medicare Coverage |
|---|---|
| Routine Checkups | Generally covered |
| Surgical Procedures (e.g., appendectomy) | Usually covered if medically necessary |
| Hospitalizations | Covered based on eligibility and length of stay |
| Diagnostic Tests (e.g., X-rays, blood tests) | Usually covered if medically necessary |
| Experimental Treatments | Usually not covered |
Medicare Coverage for AFib Ablation
Medicare’s AFib ablation coverage isn’t a simple yes or no. It depends on a lot of factors, from the specific reason for the procedure to the documentation your doctor provides. Navigating this can feel tricky, but understanding the rules can help you get the care you need.Medicare’s coverage decisions for AFib ablation are based on whether the procedure is deemed medically necessary for treating the condition and preventing complications.
It’s not just about the ablation itself; it’s about the underlying reasons for the procedure.
Specific Circumstances for Medicare Coverage
Medicare generally covers AFib ablation if it’s deemed medically necessary to treat or prevent complications associated with AFib. This means your doctor must clearly document that the ablation is the most appropriate and effective treatment option compared to other, less invasive, methods. Factors considered include the severity of your AFib, the impact on your daily life, and the potential for long-term benefits.
For instance, if AFib is significantly affecting your quality of life or causing severe symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath, ablation might be considered medically necessary.
Role of Physician Documentation
Accurate and comprehensive physician documentation is critical for successful Medicare claims. The documentation should clearly explain the diagnosis, the rationale for choosing ablation over other treatment options, the expected benefits, and any potential risks. Detailed records of the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and any diagnostic tests performed (like EKGs or echocardiograms) are essential. This thorough documentation acts as evidence that the procedure is medically necessary.
Comparison of Coverage Policies Across Medicare Plans, Does medicare cover ablation for afib
Medicare Advantage plans, which are private plans that supplement Medicare, may have varying coverage policies for AFib ablation. These plans are not required to follow the same guidelines as Original Medicare. It’s essential to review your specific plan’s policy to understand what’s covered and any potential out-of-pocket costs. Original Medicare, Part B, generally covers the procedure if deemed medically necessary by the physician.
Differences can arise in the pre-authorization requirements and the specific types of ablations covered.
Impact of Pre-authorization Requirements
Pre-authorization requirements can significantly impact coverage for AFib ablation. Some Medicare plans require pre-authorization before the procedure. This involves submitting a request to the plan outlining the medical necessity for the procedure. If pre-authorization is needed, you’ll need to provide detailed information supporting the request, and the plan may request additional documentation. This step is often necessary for Medicare Advantage plans to ensure the procedure aligns with their coverage guidelines.
Examples of Successful and Rejected Claims
A successful claim might involve a patient with severe, symptomatic AFib who demonstrates a clear need for ablation. Comprehensive documentation supporting the medical necessity and potential long-term benefits would be critical. Conversely, a rejected claim might involve a patient with mild AFib symptoms, and the documentation lacks sufficient evidence to support the medical necessity of the ablation.
Table: Medicare Plan Coverage Policies
| Medicare Plan Type | Typical Coverage Policy for AFib Ablation |
|---|---|
| Original Medicare (Part B) | Generally covers if medically necessary, but may require pre-authorization in some cases. |
| Medicare Advantage Plans | Coverage varies; review your specific plan’s policy. May have more stringent pre-authorization requirements. |
Factors Affecting Coverage Decisions
Medicare’s AFib ablation coverage isn’t a simple yes or no. It’s a nuanced evaluation considering several factors, making it crucial to understand the process. The good news is, with the right info, you can better navigate this.The decision-making process for Medicare coverage of AFib ablation is multifaceted. It goes beyond just the procedure itself and looks at the patient’s whole health picture.
This means looking at everything from your overall health to the severity of your AFib and how it affects your daily life. The physician’s recommendation and documentation are also key pieces of the puzzle. Let’s dive deeper into these critical elements.
A shadowed query hangs heavy, a whispered plea: does Medicare cover ablation for AFib? The rhythm of life, fractured and strained, seeks solace in the echoes of forgotten melodies. Perhaps the answer lies within the monumental sounds of the Amon Amarth tour 2024 setlist, a testament to the strength found in the face of uncertainty. Yet, the heart, weary and aching, still seeks clarity on the path to healing.
Does Medicare, in its profound wisdom, grant relief from this arrhythmic torment? The answer, elusive and subtle, remains veiled in the mists of medical mystery.
Patient’s Overall Health Status
Patient health plays a huge role in Medicare’s coverage decisions. A comprehensive health assessment, including pre-existing conditions, overall wellness, and current medications, heavily influences the coverage determination. Factors like the presence of other significant health issues can affect the feasibility and potential risks associated with the procedure. For example, someone with severe heart failure might be deemed a higher risk for ablation, potentially impacting coverage decisions.
Severity of AFib and Impact on Quality of Life
The severity of AFib and its impact on a patient’s quality of life are also considered. Does AFib significantly impair daily activities, leading to fatigue, reduced mobility, or other quality-of-life issues? If so, this could strengthen the case for coverage. Medicare often looks at the frequency and duration of AFib episodes, and the effectiveness of other treatments.
For example, a patient experiencing frequent and debilitating AFib episodes that significantly impact their daily life has a stronger case for coverage than someone experiencing infrequent episodes that don’t significantly impair their quality of life.
Treating Physician’s Recommendations and Documentation
The treating physician’s recommendations and detailed medical documentation are crucial. The physician’s assessment of the necessity of the ablation procedure, along with a thorough explanation of the potential benefits and risks, is essential. Comprehensive documentation of the patient’s condition, including a detailed history, ECG results, and other relevant tests, should be meticulously recorded. For example, if the physician strongly recommends the ablation based on the patient’s specific situation and provides detailed evidence supporting their recommendation, this greatly strengthens the case for coverage.
This documentation should be thorough and clearly articulate the reasoning behind the procedure.
Prior Authorization Requests and Appeals Process
Prior authorization requests are often required for Medicare-covered procedures, including AFib ablation. Understanding the process and submitting the necessary paperwork promptly is critical. If coverage is initially denied, the appeals process can be initiated. The appeals process allows patients to contest the denial, providing further evidence and reasoning for the necessity of the procedure. For example, a well-documented appeal with compelling evidence, including expert opinions and additional testing results, can increase the chances of successful appeal.
Examples of Coverage Decisions
Coverage decisions aren’t always straightforward. A patient with well-controlled AFib, experiencing only occasional episodes that don’t impact their quality of life, might be denied coverage. On the other hand, a patient with severe AFib that significantly impacts their daily life and for whom other treatments have failed, might have their coverage approved. These decisions are often made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account all the factors mentioned previously.
For instance, if the physician’s documentation clearly shows the ablation as a reasonable and necessary treatment option given the patient’s specific condition and the failure of other treatments, this can significantly improve the chances of approval.
Navigating the Medicare Coverage Process for AFib Ablation: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Consultation with your physician: Thoroughly discuss your AFib condition, treatment options, and the necessity of ablation with your physician.
- Gathering medical records: Collect all relevant medical records, including prior medical history, ECG results, and any other relevant testing data.
- Understanding Medicare coverage criteria: Research Medicare’s guidelines for AFib ablation coverage.
- Completing prior authorization requests: Submit the prior authorization request, following the instructions and guidelines provided by Medicare.
- Appealing denials (if necessary): If coverage is initially denied, understand the appeals process and follow the necessary steps to appeal the decision.
- Staying informed: Keep updated on any changes or updates in Medicare coverage guidelines for AFib ablation.
Illustrative Examples of Medicare Coverage
Medicare’s AFib ablation coverage isn’t a simple yes or no. It depends on a bunch of factors, like the patient’s overall health, the specific procedure, and the reason for the ablation. Let’s look at some real-world examples to get a clearer picture.
Medicare-Covered AFib Ablation
Medicare coverage for AFib ablation often hinges on the severity of the AFib and whether the procedure is deemed medically necessary. A good example would be a patient with frequent, debilitating AFib episodes that significantly impact their daily life. If their AFib isn’t responding to other treatments like medication, and the ablation procedure is deemed essential to restore normal heart rhythm, Medicare is likely to cover the procedure.
Example Case 1: A 65-year-old patient with chronic AFib experienced frequent episodes of rapid heartbeats, leading to fatigue and shortness of breath. Traditional medications failed to effectively control their symptoms. An AFib ablation was performed, and the procedure successfully restored a normal heart rhythm. Medicare covered the procedure, as the ablation was deemed medically necessary to alleviate the patient’s severe symptoms and improve their quality of life.
The heart’s erratic beat, a troubled drum, echoes questions of medicare’s hand in covering afib ablation. Searching for answers, one stumbles upon the somber pages of Frederick Dean Funeral Home obituaries , a poignant reminder of life’s fleeting nature and the delicate balance within. Yet, amidst the sorrow, the question lingers: does medicare indeed cover this procedure to mend the heart’s rhythm?
The uncertainty hangs heavy, a shroud over the soul’s inquiry.
Example Case 2: A 72-year-old patient with pre-existing heart conditions underwent an AFib ablation for symptomatic AFib. The patient experienced chest pain and dizziness from the arrhythmia. The ablation procedure was deemed essential to address these debilitating symptoms, and Medicare covered the procedure, given the patient’s specific medical history and the procedure’s potential to alleviate their symptoms.
Medicare Non-Coverage of AFib Ablation
Medicare might deny coverage for an AFib ablation if it’s not considered medically necessary or if the patient’s symptoms are deemed manageable with other treatments. This could involve cases where the patient’s AFib isn’t causing significant health problems or if the patient is not a suitable candidate for the procedure.
Example Case 1: A 78-year-old patient with mild AFib symptoms, who experience only occasional and mild discomfort, had an ablation procedure requested. Medicare denied coverage as the patient’s symptoms were deemed manageable with medication and lifestyle changes. The patient had the option to appeal the decision, demonstrating their disagreement with the coverage denial.
Example Case 2: A patient with a history of multiple heart surgeries and significant pre-existing health conditions sought an AFib ablation. Medicare denied coverage as the procedure’s potential benefits were outweighed by the high risks associated with the patient’s complex medical profile. The patient’s options included exploring alternative treatments and potentially appealing the decision if the procedure is deemed medically necessary.
Real-Life Case Study: AFib Ablation
A 55-year-old patient with a history of hypertension and diabetes developed persistent AFib. Their AFib episodes were impacting their daily life, causing extreme fatigue and anxiety. They underwent an AFib ablation procedure, which successfully restored a normal heart rhythm. Medicare covered the procedure because the ablation was deemed medically necessary to alleviate the patient’s debilitating symptoms. The procedure was deemed safe for this patient’s medical condition.
Medicare Official Statement on Coverage Policies
“Medicare coverage for AFib ablation is determined on a case-by-case basis, considering the patient’s specific medical condition, the severity of their AFib, and the potential benefits of the procedure compared to the risks. Factors like the patient’s overall health, response to other treatments, and the potential for long-term improvement are all considered in the decision-making process.”
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding Medicare’s coverage for AFib ablation requires careful consideration of various factors. The patient’s health status, the severity of AFib, and physician recommendations play crucial roles. Thorough preparation, including pre-authorization requests and awareness of the appeals process, can significantly influence the outcome. This comprehensive guide provides the necessary information to navigate the complexities of Medicare coverage for AFib ablation, empowering patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Expert Answers
What are the common types of AFib ablation procedures?
Various techniques exist, each with potential benefits and risks. Understanding the different types helps patients discuss options with their healthcare provider.
How does the severity of AFib affect coverage decisions?
The severity of AFib and its impact on the patient’s quality of life are crucial factors. A more severe case may be more likely to be covered.
What role does physician documentation play in coverage decisions?
Detailed and comprehensive physician documentation is essential. This documentation should clearly demonstrate the necessity and appropriateness of the ablation procedure.
What resources are available to patients navigating Medicare coverage issues?
Numerous organizations offer support and resources to patients. Consult your doctor or local healthcare authority for a list of available resources.
